Cybersecurity
May 16, 2022
COC Cybersecurity
KNOWING, HAVING, BEING – COMBINING MULTI-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION CORRECTLY
Protect your data with multiple factors!
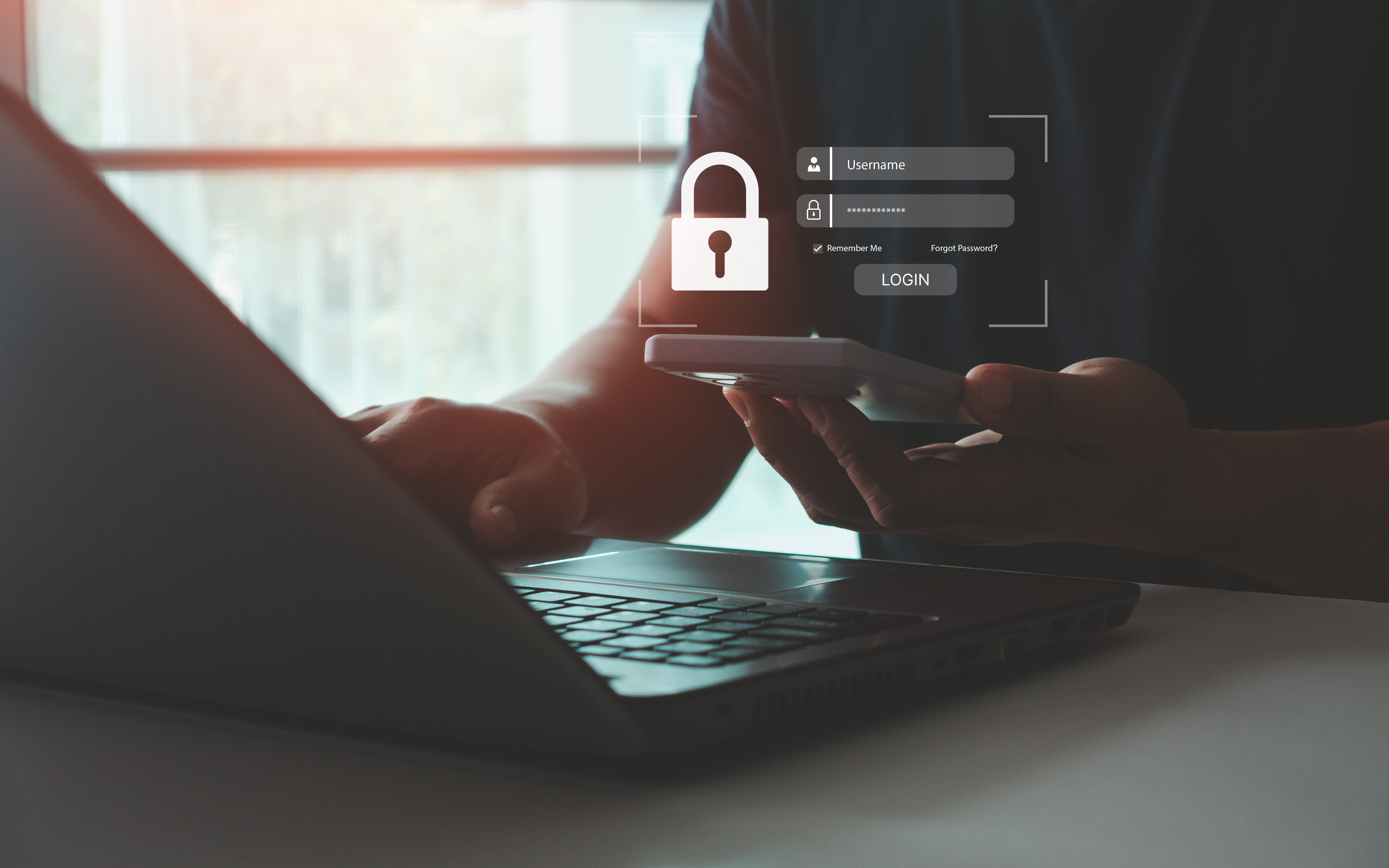
What is multi-factor authentication?
As the name suggests, multi-factor authentication is the proof of identity on several levels – i.e. the proof of a user's access authorization to a system.

The fact that login data is stolen by phishing and/or passwords are negligently disclosed to third parties is certainly nothing new to you. In the case of an access restriction that is protected by only one factor – the most common protection here is the username-password principle – access can be granted directly after a successful phishing attack.
But how can you use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to make your company infrastructure more secure and better protect your company data?
The Three Types of Multi-Factor Authentication
Of course, it makes no sense to use two passwords that you enter one after the other for one access. Security would only increase minimally, as both passwords can also be "phished". It is better to restrict access to several independent ways. For this reason, the different factors of multi-factor authentication are divided into the three common types:
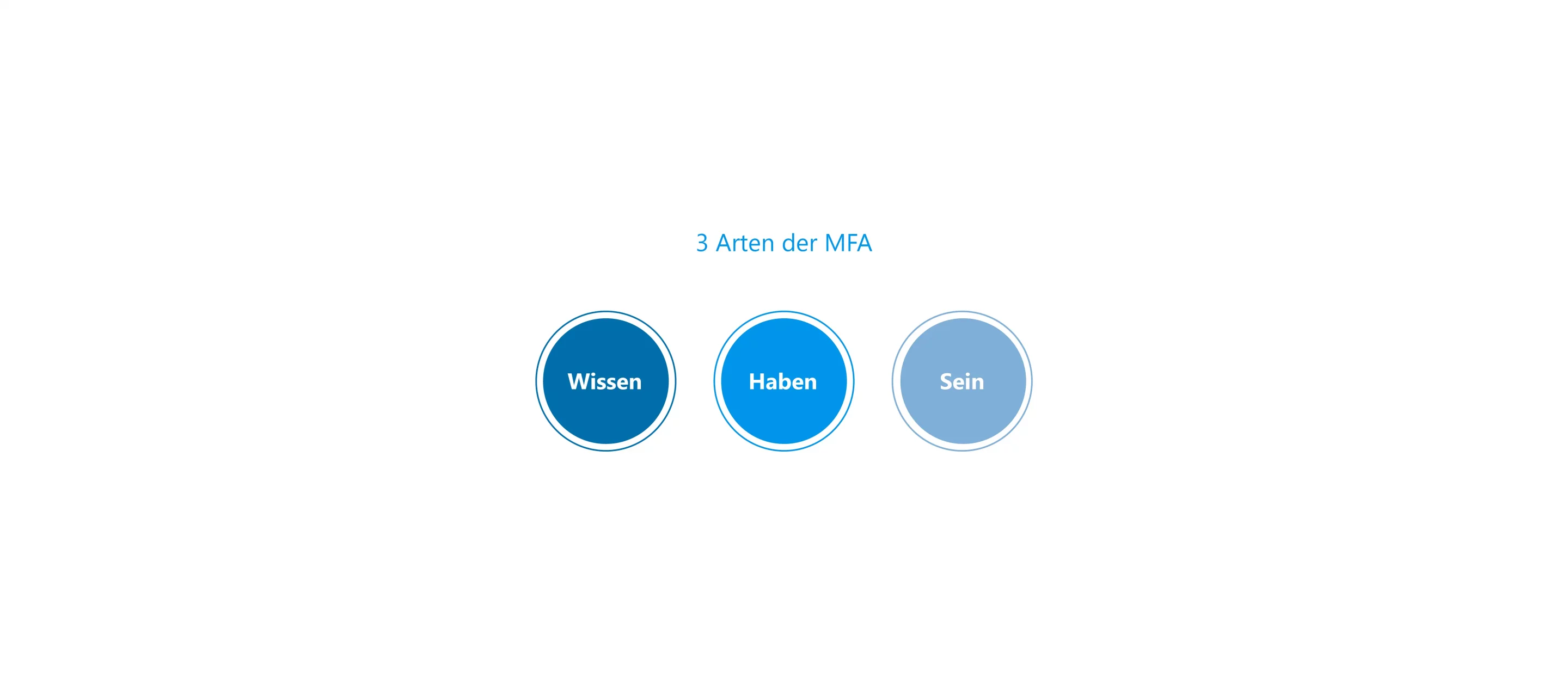
- Knowledge (which only the authorized person has)
- To have (physical possession)
- and Being (Inherence)
What is "knowledge"?
Secret knowledge is the most commonly used factor for identity verification. Passwords, security questions or entering PIN codes are the most common methods of authentication for logging into the mailbox, unlocking Bitlocker hard disk encryption or logging into the HR management system for time tracking or picking up the payslip. This secret knowledge must only be known to the user himself.
Do you already know how to create strong passwords that everyone can easily remember? You can read the relevant article here.
What is "having"?
With authentication through physical possession, a user can confirm his identity, e.g. by a chip card, a token, but also by his smartphone with a unique phone number. There are various smartphone applications (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator) and hardware devices (YubiKey, SecurID token) that can be used for this purpose.
What is "being"?
Inherence authentication leverages a user's unique physical characteristics. Biometric data such as fingerprint, iris or voice are characteristics that are unique to each person and can identify a user in a largely forgery-proof manner. Many laptops and smartphones now have built-in fingerprint scanners or use the camera for facial recognition. To date, no two people are known to have the same fingerprint.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each factor?
Have you ever seen a password written down on a post-it and taped to the edge of the screen? Despite all the warnings, this method of facilitating access still occurs. All knowledge can be forgotten. Knowledge can be passed on just as easily, intentionally or unintentionally. While entering a password, PIN, security pattern, or answering a security question is easy, the method of authentication is also insecure—especially if it's the only method.
The situation is different with ownership. The property cannot simply be forged or "phished". It would have to be physically stolen. The disadvantage is that the property can also be lost or forgotten.
Because physical features are unique, they cannot be imitated by strangers. These authentication methods also consist of complex data sets (fingerprint, iris, voice), but adapted hardware is needed to record them. In addition, intimate physical characteristics are stored. Loss of these physical features, such as an amputated thumb, can void access authorisations.
Only the combination of two or more factors ultimately gives you increased security and optimal protection of your company data.
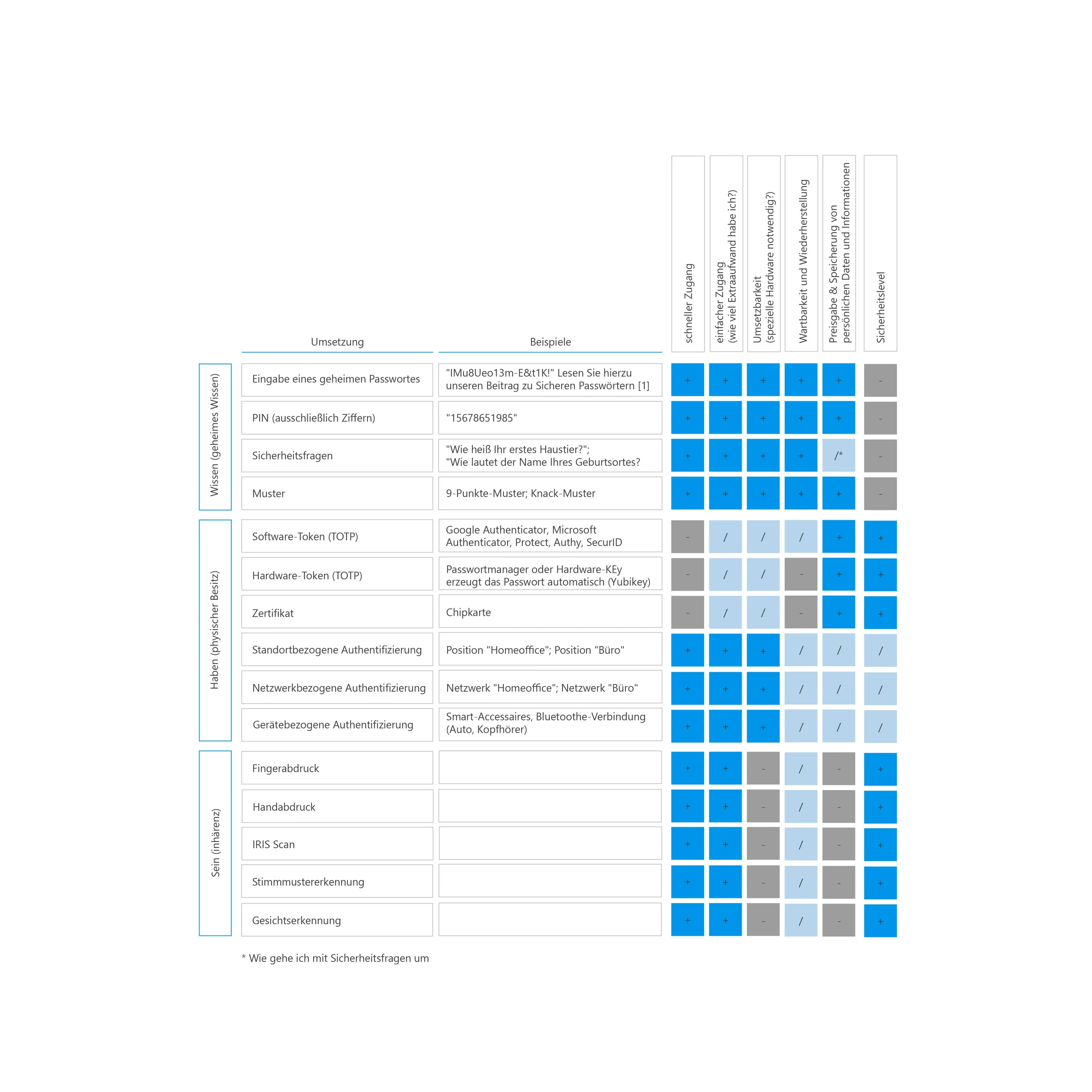
In the following overview, we present various options for implementing multi-factor authentication and compare them based on selected criteria.
How does multi-factor authentication work in practice?
The first and most common login factor of a user is the entry of a secret password or PIN, which may only be known by the user himself. If the user was able to authenticate himself correctly by entering the data, he is asked to authenticate himself again with the second factor. In the second stage, an additional PIN is generated by a second device. A hardware token or an authenticator app can be used on the company phone to display the PIN code. Automatic login hardware, which generates an unknown new one-time password (OTP) for the user, can also be used as a second factor for login.
It is important to note that two factors of different classes are necessary when registering the user. As in the example mentioned, secret knowledge (knowledge) and physical possession (having).
If both factors have been authenticated by the system, the user receives access to company emails and data. For an unauthorized third party who has come into possession of the password, there is little possibility to bypass the authentication process and thus gain access to sensitive company data without access to the second necessary factor.
The classic combination of two factors used in practice, the password (knowledge) and the token (credit), is referred to as two-factor authentication, or two-factor authentication. In everyday life, you know this example in the combination of bank card (credit) and PIN (knowledge). Of course, you can also opt for more than two factors and increase security with a third factor. This method is also known as 3FA.
As you have probably already noticed, the combinatorics of the various factors are not equivalent. When using two or more factors, there are more sensible and less sensible combinations. So how do you combine individual authentication factors correctly?
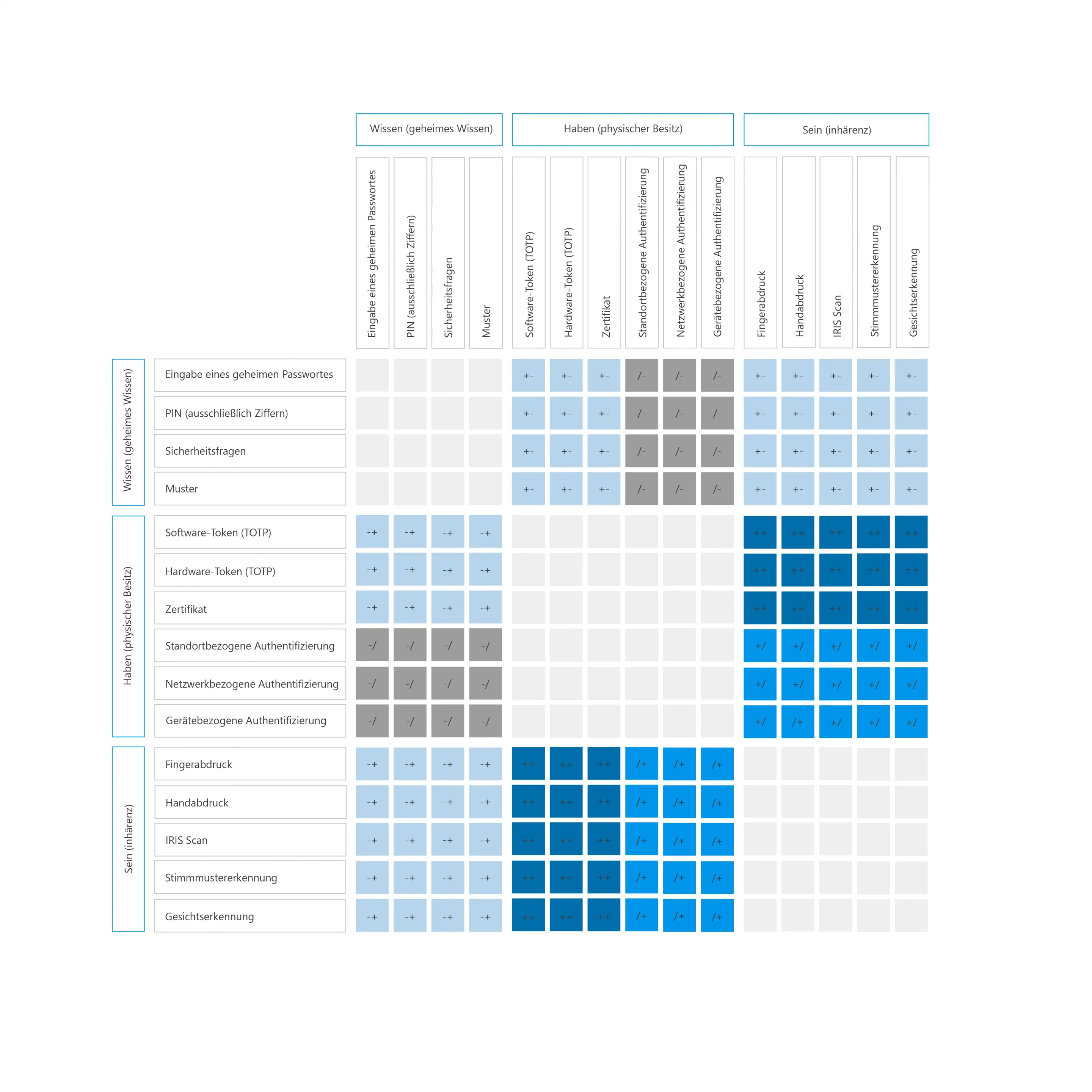
The following table shows you the ratio of security to the selected combination:
Where do I start?
We are also happy to support your company with our Cybersecurity Awareness training, in which we highlight risks and use simple tips to teach your employees what they can and must do themselves to ensure the protection of your company in the digital world. For different application scenarios, we support you with technical and organizational measures. Depending on your company structure, we establish everything from password guidelines to hardware token mechanisms for security.
In addition, we offer you the entire range of security instruments in a framework from a single source, from code reviews of your software products, quick checks of your organization, awareness training of your employees to penetration testing of your servers and IT landscape, and support you in the implementation of your individual holistic cybersecurity plan.
Together we master the future!
Written by:
COC Cybersecurity
Contact